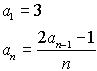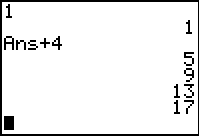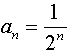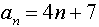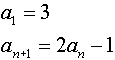|
Working with Sequences
(in both Seq
and Func Modes) |
|
To work with sequences in the Seq mode:
-
Press MODE key
-
Choose Seq in the fourth line
-
Hit ENTER to highlight Seq
-
Leave other settings as default (on the
left side)
|
 |
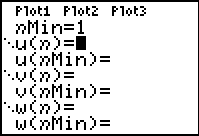
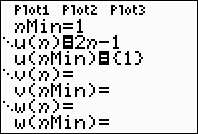
Press Y= and notice the difference in
this screen.
To define a sequence, you must
specify:
- nMin -
where you will start counting the numbers
in the sequence (most
likely this value is 1)
- u(n) - the
pattern for the sequence
(use 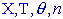 key to enter the pattern) key to enter the pattern)
- u(nMin) - the
first number in the sequence
(When you enter the first number in your
sequence, notice the list braces that appear. These braces
will allow for
the entry of more than one term if needed.)
|
 |
Example 1: Consider
the sequence defined as 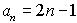 . .
List the first 6 terms of the sequence and find the 105th term.
|
Enter the information in Y=:
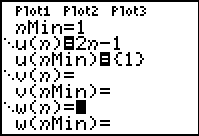 |
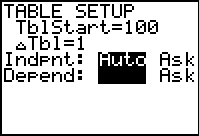
Set the table (TBLSET):
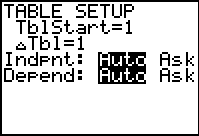 |
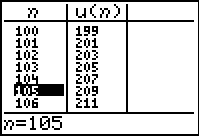
Look at the table (TABLE):
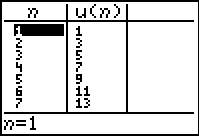 |
The first 6 terms are easily visible in the table.
To find the 105th term, reset the
TblStart to a value near (or at)
the desired term.
Read the answer from the table. |
If you
GRAPH when in
sequence mode, even if your calculator
is set in connected mode, you will
only see plots of points. Remember that a sequence is a
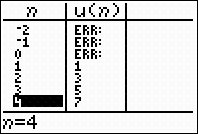
listing of numbers without other values in between. Notice, in the
center calculator screen below, how the sequence
mode table shows answers only for n values of 1 or larger.
Remember that the domain of a sequence is the set of natural numbers
{1, 2, 3, ...}.
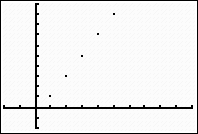
If you express this sequence as a function and return to function mode, you will see a connected graph (a line in this
case), rather than the plotted points.
Example 2: (Recursive sequence)
List the first 7 terms of the sequence:
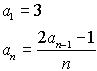
|
Enter the recursive formula information.
Enter the u by using the alpha letter u
(2nd 7). Note the starting value of
3.
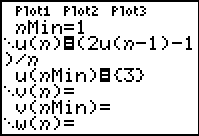 |
View the terms of the sequence
in the table.
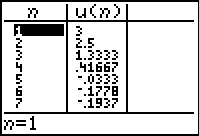 |
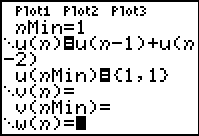
Example 3: Generate the Fibonacci Sequence (where each term, after the first two terms, is
determined by adding the two previous terms).
|
Enter the pattern for the sequence.
Notice how the u(nMin) displays
the first two terms using the
list braces.
 |
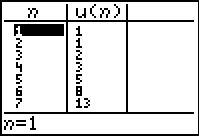
Go to the table to view the
Fibonacci sequence.
 |
| Certain sequences can be examined in Func mode. Consider the
following examples: Example 4: Arithmetic
and geometric sequences can be quickly generated in
Func mode if the
common difference or common ratio, respectively, are known, along with
the starting value. |
 |
List the first five terms of an arithmetic sequence whose
first term is 1 and whose common
difference is 4.
A "quick - see it on the screen" method:
- Enter the first term on the home screen.
- Press ENTER to
register the first term.
- Press + 4
(the expression Ans+4 will appear).
- Press ENTER.
- Continuing to press ENTER
will generate successive terms in this sequence.
|
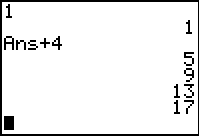 |
|
Unfortunately, finding specific terms
with this method, such as the 100th,
will require that you press ENTER and count very carefully - not
always an easy process. |
|
Example 5: If an expression/formula is known for the
generation of a sequence, the terms can be listed in
Func mode using the seq( function.
List the first 6 terms of the sequence defined by: 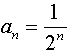
|
2nd STAT (LIST)
→ OPS
Choose #5 seq( |
Using seq(, type the formula, variable, starting
value
for n, last value of
n needed, increment.
(For ease, X may
be used as the variable --
or type N
using the alpha key.)
Arrow to the right to see
more of the terms
of the sequence.
If you need fractional answers,
utilize the
MATH - #1►Frac
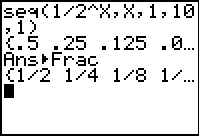 |
This method of listing terms of a sequence will be
limited
to 999 terms of the sequence at any one time.
Example 6: If an expression/formula is known for the
generation of a sequence, the sum of a specific number of terms can be
found in Func mode.
Find the sum of the first 10 terms of the sequence defined
by: 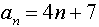
|
2nd STAT (LIST)
→ MATH
Choose #5 sum(
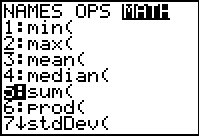 |
Notice that sum
is followed by the entry
of the sequence as shown in Example
5.
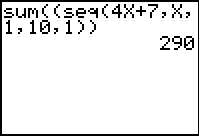 |
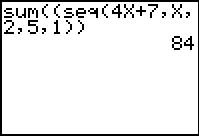
Find the sum of the second through fifth terms of the
sequence: 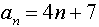
Example 7: Sequences represented by a recursive formula can be
generated in Func mode.
List the first 4 terms of the sequence defined by: 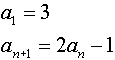
| |
-
Type the starting value
and press ENTER.
-
Use the
ANS function to create the
formula used to generate the sequence. Type
2*ANS-5 and press
ENTER.
-
Now, simply press
ENTER to create successive
terms of the sequence.
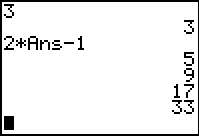
|

Finding
Your Way Around TABLE of CONTENTS
|